Small Molecule Drug Discovery for Longevity: Current Breakthroughs and Clinical Pipeline 2025
By The Pauling.AI Team.
The global anti-aging market surpassed $85 billion in 2025, reflecting a fundamental shift toward treating aging as a targetable biological process.
Small molecule drug discovery for longevity is transitioning from theory to clinical reality, driven by computational advances and deeper mechanistic understanding.
What Makes Small Molecules Ideal for Longevity Interventions?
Small molecules organic compounds under 900 daltons offer distinct advantages for longevity interventions: oral bioavailability, cellular membrane permeability, and the ability to modulate multiple aging pathways simultaneously. Unlike biologics, they’re easier to manufacture and can target intracellular processes.
A 2025 study in Aging Cell demonstrated that AI-designed polypharmacological compounds achieved 70% lifespan extension in C. elegans [1]. This remarkable finding suggests that targeting aging’s multifactorial nature through compounds acting on multiple pathways may be more effective than single target approaches.
Separately, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute identified another critical target: mitochondrial energy production. By enhancing respiratory supercomplex function, researchers extended both lifespan and healthspan in mice [2] proving that cellular powerhouses aren’t just metaphors, they’re druggable longevity targets ripe for small molecule intervention.
mTOR Inhibitors, Senolytics, and Metabolic Modulators: The Longevity Trio
mTOR Inhibitors
Rapamycin remains the most reliable lifespan extender across model organisms, according to the National Institute of Aging's Intervention Testing Program [3]. A 2025 Oxford study revealed that rapamycin protects human T cells from DNA damage and increases survival threefold, providing mechanistic evidence for geroprotective effects [4]. Next-generation compounds like rapalink-1 are showing promise in extending lifespan while revealing connections between mTOR signaling, metabolism, and microbiome composition [5].
Senolytics: Eliminating “Zombie Cells”
As we age, senescent cells often called “zombie cells” accumulate and fuel chronic inflammation. Can we selectively eliminate them? A landmark Harvard-Mayo-Cedars-Sinai study proved dasatinib plus quercetin is safe in older adults, reducing inflammatory markers and improving memory [6]. AI is accelerating discovery: machine learning models identified four potent compounds JQ1, RG7112, AMG232, and nutlin-3a that target both epigenetic age and senescence markers [7]. Second-generation agents like navitoclax and FOXO4-DRI peptides now offer even greater precision [8].
Metabolic Modulators: The Diabetes Drugs That Slow Aging
GLP-1 receptor agonists have emerged as potential longevity therapeutics beyond diabetes treatment, improving mitochondrial function and reducing inflammation [3]. A 2024 Cell study showed metformin’s geroprotective effects in monkeys, enhancing cognitive abilities [9]. Recent preclinical work combining oxytocin with an Alk5 inhibitor boosted lifespan in elderly male mice by 70%, highlighting sex-dependent aging responses [10].
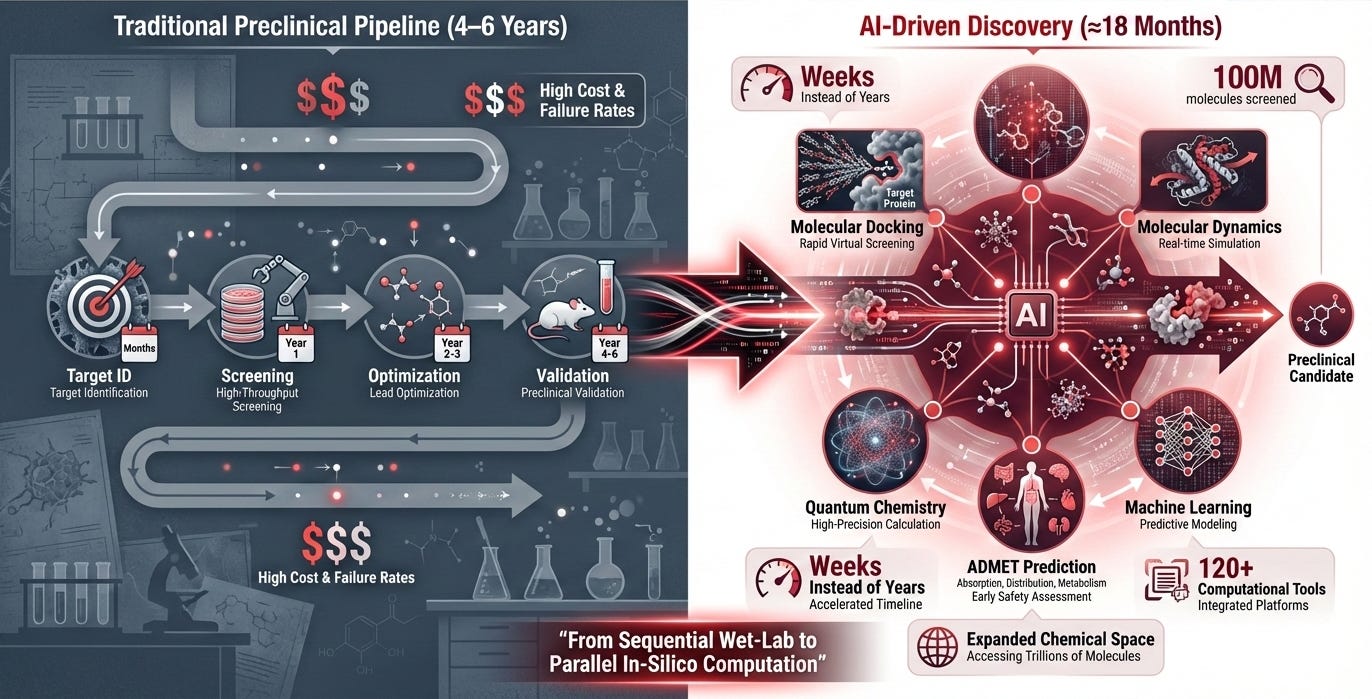
From 4 Years to 18 Months: The AI Drug Discovery Advantage
Computational chemistry is transforming longevity drug development. Traditional pipelines require 4-6 years for preclinical work costing hundreds of millions; computation chemistry advanced methods such as ML are compressing timelines dramatically.
Pauling.AI’s autonomous platform integrates 120+ computational tools spanning six categories from RCSB Protein Data Bank structures, target modeling with AlphaFold, Boltz and RosettaFold to molecular dynamics engines like GROMACS with free energy analyses (dG) enabling pharma partners to identify viable candidates in weeks rather than years[11].
How does this speed happen? Modern AI platforms orchestrate multiple computational techniques simultaneously [12]. Molecular docking through tools like AutoDock Vina, GNINA, and Glide predicts which compounds bind target proteins. Molecular dynamics simulations using AMBER, CHARMM, and OpenMM map conformational changes across time scales. Quantum mechanics calculations via Gaussian, ORCA, and CP2K optimize drug properties at the atomic level. Machine learning models predict ADMET profiles (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) before synthesis. What once required sequential wet-lab experiments now happens in silico, in parallel, at computational speed.
Comprehensive platforms like Autochem by Pauling.AI, one of our main AI agents orchestrating 120+ computational tools across target modeling, pocket druggability assessment, docking, molecular dynamics, FEP, and structural analysis enable extensive in silico screening before synthesizing compounds dramatically reducing costs and failure rates.
Quantum-classical hybrid computing is expanding accessible chemical space beyond traditional methods. A 2025 collaboration used quantum circuit Born machines with deep learning to screen 100 million molecules, identifying compounds with genuine biological activity against KRAS-G12D, a notoriously difficult cancer target [13]. AI-driven polypharmacology intentionally designing compounds targeting multiple aging pathways reflects aging’s multifactorial nature. This approach achieved a 70% hit rate in validating lifespan extension, far exceeding traditional single-target screening success rates [1].
What's Holding Us Back? And What's Next?
Despite progress, three critical barriers block widespread deployment. First, senescent cells aren’t uniform different tissues require tailored interventions [8]. Second, we lack validated aging biomarkers that actually reverse upon treatment [14]. Third, the safety paradox: senolytics must eliminate harmful senescent cells without disrupting their beneficial roles in wound healing and tumor suppression.
The solution? Think bigger. In a recent conversation between longevity pioneer Aubrey de Grey and our CEO Javier Tordable, de Grey emphasized that treating the body as a maintainable machine repairing accumulated damage through combination therapies remains central to achieving what he terms “longevity escape velocity.”
This concept suggests that advances in therapeutic technology could progress rapidly enough that people remain biologically younger as they age chronologically. They highlighted how advanced ML and CRISPR are accelerating damage repair strategies, though comprehensive funding and integrated approaches remain critical challenges.
They project significant breakthroughs by the end of the 2030s, aligning with the timeline for precision senotherapy guided by single-cell aging atlases and AI diagnostics [15].
Researchers are already proposing targeted nanoparticle delivery of therapeutics to specific tissues. The FDA’s 2025 draft guidance on AI in drug development, informed by 500+ submissions, reflects evolving regulatory frameworks [11]. As quantum computing advances exemplified by Microsoft’s Majorana-1 chip convergence of AI, quantum methods, and experimental validation will accelerate first-in-class longevity therapeutics [13].
Watch the full conversation on longevity research with Aubrey De Grey and the future of aging therapeutics on the Pauling.AI YouTube channel.
Comp Chem Isn’t Optional Anymore, It’s Central!
We’ve crossed a threshold. Small molecule longevity drug discovery is no longer theoretical it’s translational, with compounds advancing through clinical trials as you read this. The evidence is quantifiable: Drug discovery compressed from 4-6 years to 18 months for under $2.6 million [11]. AI-designed polypharmacological compounds achieved 70% lifespan extension in preclinical models [1]. Dasatinib plus quercetin demonstrated safety and cognitive benefits in human trials [6].
Computational chemistry platforms like Autochem, our main AI-agent orchestrating 120+ tools across molecular docking, dynamics simulations, FEP, and machine learning [12] are the engine driving this acceleration. These aren’t incremental improvements. Quantum-classical hybrid computing is expanding chemical space exponentially, identifying compounds against previously “undruggable” targets [13].
The FDA has processed 500+ AI-assisted drug applications since 2016 [11].
The goal isn’t just more years, it’s more healthy years. And computational chemistry is making longevity escape velocity measurable, achievable, and closer than the field has ever been.
Stay at the Forefront of Longevity Science
The intersection of AI and drug discovery is evolving rapidly. Subscribe to our news to receive insights on computational chemistry breakthroughs, small molecule therapeutics, and how AI is accelerating the development of next-generation longevity compounds.
Join researchers, biotech professionals, and innovators shaping the future of healthspan extension.
References
[1] Fedichev, P. et al. (2025). “AI-designed polypharmacological compounds show promise in lifespan extension.” Aging Cell. https://longevity.technology/news/ai-designed-compounds-show-promise-in-lifespan-extension/
[2] Ikeda, K. et al. (2025). “Mitochondrial Respiratory Supercomplex Assembly Factor COX7RP Contributes to Lifespan Extension in Mice.” Aging Cell. DOI: 10.1111/acel.70294. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/12/251218060557.htm
[3] Getchell, M. et al. (2025). “Top 10 Longevity & Anti-Aging Breakthroughs of 2025.” Healthspan. https://www.gethealthspan.com/research/article/top-ten-longevity-anti-aging-breakthroughs-of-2025
[4] Kell, L.B. et al. (2025). “Rapamycin exerts its geroprotective effects in the ageing human immune system by enhancing resilience against DNA damage.” bioRxiv 2025.08.15.670559. https://www.nad.com/news/new-oxford-study-powerful-longevity-drug-rapamycin-targets-cell-senescence
[5] Kumar, J., Ng, K., & Rallis, C. (2025). “Rapalink-1 reveals TOR-dependent genes and an agmatinergic axis-based metabolic feedback regulating TOR activity and lifespan in fission yeast.” Communications Biology, 8(1). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08731-3. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/12/251205054729.htm
[6] Millar, C.L. et al. (2025). “A pilot study of senolytics to improve cognition and mobility in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease.” Harvard-Mayo-Cedars-Sinai Joint Study. https://www.nmn.com/news/new-harvard-study-anti-aging-senolytics-are-safe-for-seniors-with-memory-loss
[7] Springer Nature Research Communities. (2025). “Senolytics and the longevity of healthy humans.” https://communities.springernature.com/posts/senolytics-and-the-longevity-of-healthy-humans
[8] Zhang, Y. et al. (2025). “Targeting Senescence: A Review of Senolytics and Senomorphics in Anti-Aging Interventions.” Biomolecules, 15(6), 860. https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/15/6/860
[9] Bank of America. (2025). “Longevity Science: How Anti-aging Medicine Is Advancing.” https://business.bofa.com/en-us/content/breakthrough-technology/longevity-science-advances.html
[10] Stanford University. (2025). “Scientists boost lifespan by 70% in elderly male mice using simple drug combo.” ScienceDaily. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/12/251202052226.htm
[11] Niazi, S.K. (2025). “Artificial Intelligence in Small-Molecule Drug Discovery: A Critical Review of Methods, Applications, and Real-World Outcomes.” Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1271. https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/18/9/1271
[12] Kattuparambil, A.A. et al. (2025). “Exploring chemical space for ‘druglike’ small molecules in the age of AI.” Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 12. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1553667
[13] Model Medicines. (2025). “The Future of Drug Discovery: 2025 as the Inflection Year for Hybrid AI and Quantum Computing.” https://modelmedicines.com/newsroom/the-future-of-drug-discovery-2025-as-the-inflection-year-for-hybrid-ai-and-quantum-computing
[14] Aparicio, A. et al. (2025). “Bridging expectations and science: a roadmap for the future of longevity interventions.” PMC. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12213962/
[15] Chen, J.B., Wang, M.C., Gong, S., & Li, H. (2025). “Toward precision longevity: aging interventions in the single-cell atlas era.” Frontiers in Aging, 6. DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1674112


This article comes at the perfect time! Your piece on small molecules for longevety is so insightful, I was just thinking about the future of medicine. The bit about AI-designed compounds achieving 70% lifespan extension in C. elegans really blew my mind; it's exactly why I'm so passionate about AI. Such a cool read!